
The capability to produce a checksum in ownCloud with the Checksum app is a simple but valuable feature for checking if a file has been modified since you last viewed it. A checksum is a string of alphanumeric characters that results from running the data within a file through a cryptographic hash algorithm.
For example, a Linux user might run the md5sum terminal application through a backup file with this simple command:
The output would read something similar to “02930e459fwc0678764b091cda43dc70 cpanel-backup.tar.gz.” It doesn’t modify the file in any way. But that checksum is unique to data within the file until someone edits it.
MD5 is the most commonly used algorithm because it is fast. But it is also one of the most insecure and prone to “hash collision,” a case where two completely different files produce the same checksum, along with SHA1. The ownCloud Checksum app includes sha256, sha384, sha512 and crc32 which are all stronger.
Creating a Checksum in ownCloud
The ownCloud Checksum app is easy to use.
- Log into your ownCloud dashboard as an administrator and install the Checksum app from the marketplace.
- Select the menu button in the upper-left corner and select Files.
- To the right of any file name, select the “share” icon or horizontal ellipses (…) icon and Details. A sidebar will appear to the right with additional options.
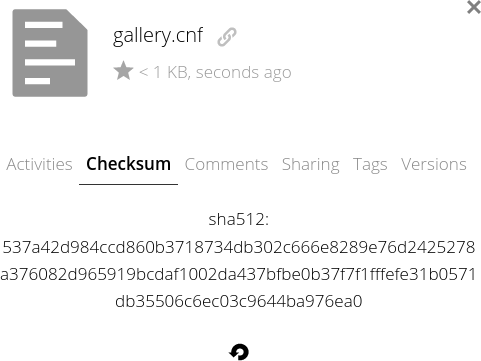
- Select the Checksum tab beside Activities.
- Select Choose Algorithm and select an option from the drop-down menu to create a checksum. We recommend using at least SHA256. For smaller files under 50 MB, a SHA512 checksum shouldn’t take longer than a few seconds.
Important Notes on Creating a Checksum in ownCloud
Strong checksums can help you indicate if a file has been modified during the upload/download process or since the last time you touched it. If you create a checksum of a file on your local machine and create a checksum once you upload the file to ownCloud, they should match if they’re made with the same algorithm (e.g. SHA256 vs SHA512).
If they don’t match, scan both files from their respective system. Try a different upload/download method – different browser, SSH, etc.
Ensure both hashes are the same algorithm. MD5 is 32 characters. SHA256 is 64 characters. SHA384 is 96 characters. And SHA512 is 128 characters.
If your team regularly uses checksums for integrity checks, store a file with all checksums in a separate location with restricted access. If someone alters the file, they shouldn’t be able to manipulate the checksums file just as easily.
Learn more from our ownCloud Education Channel.
