Table of Contents
Our article covering how to create checksums for files on your server apply to everyone using Linux as their local operating system (OS) as well. But Windows and Apple OS users would have to use different steps.
Furthermore, md5 and sha1 checksums are still popular because they’re fast. But they’re now very insecure due to the possibility of a hash collision. This means its possible for two or more completely different files to produce the same hash.
This is why we recommend more secure hashing algorithms such as sha224, sha256, sha384, and sha512 (least to most secure). Remember that creating a checksum doesn’t modify the file as you create a file hash from your computer.
Note: This is also more secure than online tools such as VirusTotal.com as you’re not uploading files externally.
If you would prefer to not use the command line or SSH to create checksums, you can use the GtkHash program, which offers a convenient graphical user interface.
Get a Checksum
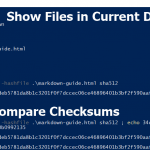
- Open your terminal
Windows MacOS PowerShell: Open the folder with the file you’ll hash, click File and Open Windows PowerShell Method 1: Click Spotlight in the upper-right ( or press ⌘ + space) and type TerminalCommand Prompt: Open the Start Menu, type cmd, and press Enter ↵.Method 2: Click Go in the menu bar, click Utilities, then Terminal Type cd \Users\your-username\Documentsto reach your file directory.
Typedirfor current directory listingType cd path-to-file-folderto navigate to the file if needed
Typelsfor current directory listing - Create the checksum
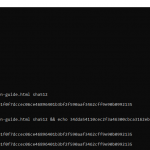
Windows MacOS certutil -hashfile path-to-file sha512shasum -a 512 path-to-fileReplace 512 with your preferred algorithm – 256, 224, 384, etc.
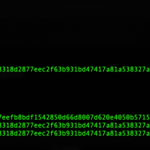
- Use the
echocommand to easily compare the two hashes
Windows MacOS PowerShell: echo hash ; echo second-hashCommand Prompt:
echo hash && echo second-hashecho hash && echo second-hash
Get more security options such as ClamAV scanner and cpHulk with our VPS Hosting.